Graphene oxide (GO) is a highly versatile nanomaterial that has gained significant attention in various scientific and industrial fields. However, to unlock its full potential, it often undergoes a process known as reduction, transforming it into reduced graphene oxide (rGO). This reduction process alters its chemical composition, structure, and properties, making it more similar to pristine graphene.
The Reduction Process
Reduction of graphene oxide involves removing oxygen-containing functional groups such as hydroxyl (-OH), epoxy (-O-), carbonyl (-C=O), and carboxyl (-COOH) groups. These groups are introduced during the oxidation of graphite to create graphene oxide, making it highly hydrophilic and insulating. By reducing these oxygen functionalities, graphene oxide regains properties similar to graphene, such as increased electrical conductivity, improved mechanical strength, and enhanced thermal stability.
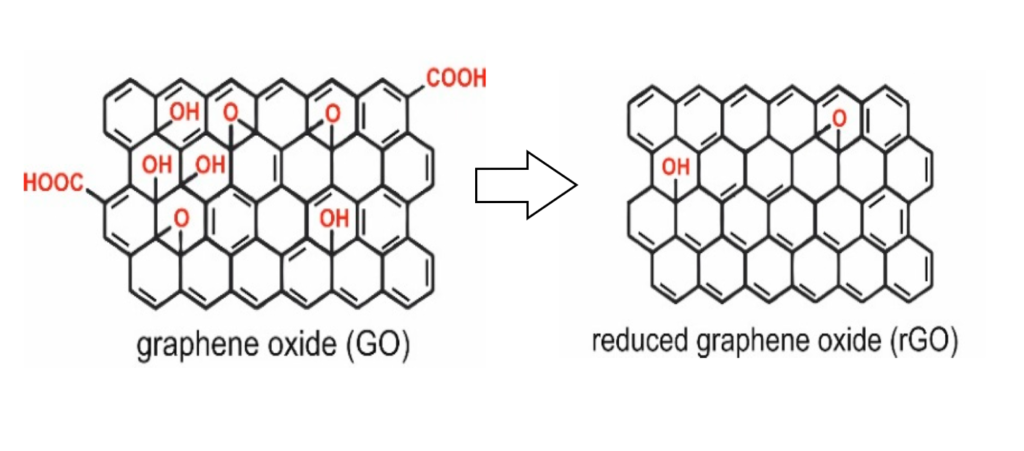
Several methods can be used to achieve this reduction:
- Chemical Reduction – Using reducing agents like hydrazine, ascorbic acid, or sodium borohydride.
- Thermal Reduction – Heating at high temperatures to remove oxygen functionalities.
- Electrochemical Reduction – Applying electrical potential to drive the reduction process.
- Photothermal and Laser Reduction – Using light or lasers to selectively remove oxygen groups.
Changes in Properties
Once reduced, graphene oxide undergoes notable transformations:
- Increased Electrical Conductivity
- The removal of oxygen groups restores the conjugated sp² carbon network, enabling better electron mobility.
- Improved Mechanical Strength
- Reduction enhances the structural integrity and mechanical properties, making rGO more durable.
- Enhanced Hydrophobicity
- While GO is water-dispersible, rGO becomes more hydrophobic, limiting its solubility but improving compatibility with certain materials.
- Higher Thermal Stability
- The reduction process increases thermal resistance, making rGO suitable for high-temperature applications.
Applications of Reduced Graphene Oxide
Reduced graphene oxide has a wide range of applications, including:
- Energy Storage: Used in supercapacitors and batteries due to its high conductivity.
- Electronics: Incorporated into sensors, transistors, and flexible circuits.
- Composites & Coatings: Added to polymers and coatings for enhanced mechanical and barrier properties.
- Water Purification: Acts as an effective material for filtration and adsorption of contaminants.
- Biomedical Uses: Employed in drug delivery and biosensing applications.
A Leading Manufacturer of Reduced Graphene Oxide
Adnano Technologies specializes in the production of high-quality reduced graphene oxide for various industrial applications. With advanced manufacturing techniques and rigorous quality control, Adnano Technologies ensures that its rGO meets the highest standards for performance and reliability. The company continues to innovate in the nanomaterials sector, offering tailored solutions for energy storage, electronics, coatings, and more.
Electrical Conductivity: One of the major benefits of rGO is its improved electrical conductivity. Unlike graphene oxide, which is an insulator, rGO exhibits enhanced conductivity, making it suitable for a variety of electronic applications, such as sensors, transistors, and supercapacitors.
Conclusion
Reducing graphene oxide is a crucial step in optimizing its properties for various applications. The transformation to reduced graphene oxide brings it closer to the characteristics of graphene while retaining some unique advantages. As research continues, advancements in reduction techniques will further enhance its performance, paving the way for more innovative applications across industries.
For more info visit : Reduced Graphene Oxide Manufacturer
