Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are among the most fascinating nanomaterials, celebrated for their exceptional mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties. Within the CNT family, single-walled carbon nanotubes called as SWCNT and multi-walled carbon nanotubes called as MWCNT are two prominent types. While both share a similar cylindrical structure made of rolled graphene sheets, they differ in their structure, properties, and applications. Let’s dive into their differences and explore how they impact our daily lives.
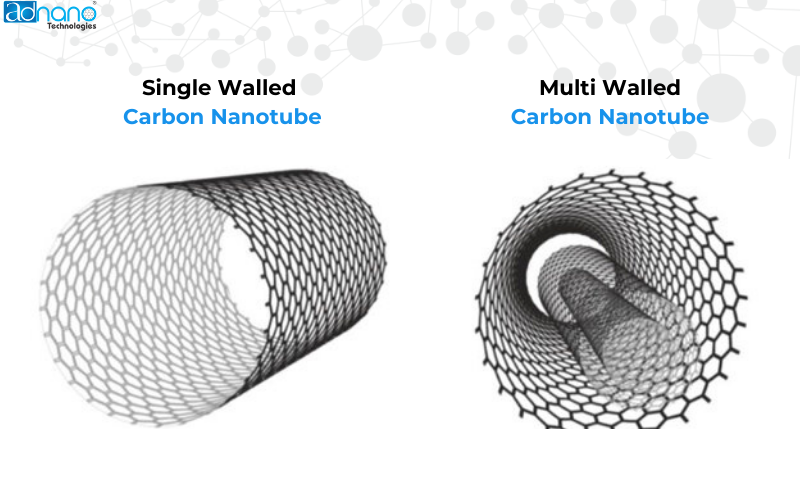
Structure of Single Walled and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes
- Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs)
- SWCNTs consist of a single layer of graphene rolled into a seamless cylinder with a diameter typically ranging from 0.8 to 2 nanometers.
- They exhibit a simple yet uniform structure, which can vary depending on how the graphene sheet is rolled form. This affects their electrical properties, making them either metallic or semiconducting.
- Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs)
- MWCNTs are composed of multiple layers of graphene rolled into cylinders looking like a nested loop.
- Their diameter can range from 2 to over 100 nanometers, depending on the number of walls, while their length can reach several micrometers.
- Due to their layered structure, MWCNTs are generally more robust but slightly less flexible than SWCNTs.
Comparison table
| Feature | SWCNT | MWCNT |
| Structure | Single-layered | Multi-layered |
| Diameter | 0.8 – 2 nm | 10 – 20 nm |
| Strength | Higher tensile strength | Comparatively lower but robust |
| Cost | More expensive | More affordable |
| Bulk Density | 0.1 g/cm3 | 0.03 g/cm3 |
Use of Single Walled and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes
The unique properties of SWCNTs and MWCNTs make them indispensable in various fields, from electronics to energy and healthcare. Here are some of their real-world applications:
1. Electronics
- SWCNTs: Their exceptional conductivity and ability to behave as semiconductors make them ideal for creating transistors, sensors, and flexible displays.
- MWCNTs: Widely used in electromagnetic shielding and as conductive additives in polymers for electronic devices.
2. Energy Storage
- SWCNTs: Used in lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors to enhance energy density and charge-discharge rates.
- MWCNTs: Commonly used as electrode materials in batteries and capacitors due to their high surface area and conductivity.
3. Composite Materials
- SWCNTs: Their lightweight and high tensile strength make them perfect for creating advanced composites for aerospace and sports equipment.
- MWCNTs: Used in car bodies, construction materials, and coatings to improve durability and reduce weight.
4. Healthcare
- SWCNTs: Explored for drug delivery systems due to their nanoscale size and biocompatibility.
- MWCNTs: Used in biosensors for detecting glucose, cholesterol, and other biomarkers.
5. Water Purification
Both SWCNTs and MWCNTs are used in filters and membranes for water purification due to their ability to remove contaminants at the molecular level.
Between SWCNT’s and MWCNT’s
The choice between SWCNTs and MWCNTs often depends on the specific application. SWCNTs are preferred for high-performance electronics and precise applications requiring semiconducting properties. In contrast, MWCNTs are more suited for bulk applications where cost and structural robustness are critical.
Conclusion
SWCNTs and MWCNTs are highly efficient materials and powering our devices to enhancing the strength of everyday materials, they’re silently shaping the modern world. As research progresses, we can expect even more innovative uses for these incredible nanomaterials, making our lives smarter, cleaner, and more efficient.
To know more : Carbon nanotubes

NICE GOOD KNOWLDGES OF MWCNT AND SWCNT