Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO) is a fascinating material derived from graphene oxide (GO), where oxygen-containing groups have been partially or entirely removed. This reduction restores many of the properties of pristine graphene, such as electrical conductivity and mechanical strength, while still allowing for some functionalization due to residual oxygen groups. Let’s dive into the details of this versatile material and its significance in cutting-edge technology.
What is Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)?
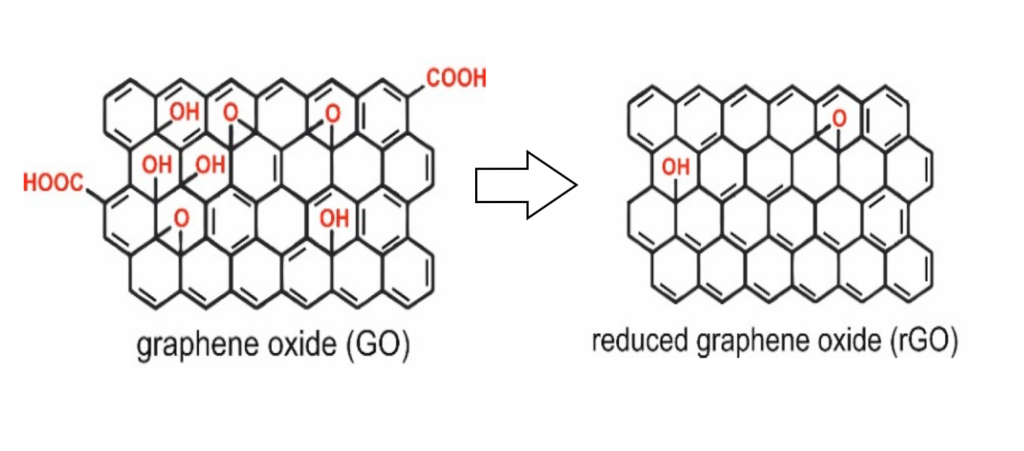
rGO is the reduced form of graphene oxide, retaining a structure closer to pristine graphene by removing oxygen-containing functional groups.
- Composition: Primarily composed of carbon with minor amounts of oxygen and hydrogen, depending on the reduction method.
- Form: Usually available in powder form, though dispersions can be created for specific applications.
Why It Matters: The reduction of graphene oxide restores many desirable properties of graphene, such as its conductivity and mechanical strength, making rGO an indispensable material in numerous applications.
How is rGO Made?
The reduction of GO into rGO can be achieved through several methods:
- Chemical Reduction:
- Common reducing agents: hydrazine hydrate, sodium borohydride, ascorbic acid.
- Operates at mild temperatures to produce rGO in a cost-effective manner.
- Thermal Reduction:
- Involves heating GO to high temperatures (above 1000°C) in an inert/reducing atmosphere.
- Produces highly conductive rGO with minimal oxygen content.
- Electrochemical Reduction:
- An electrical potential reduces GO in an electrolyte solution.
- Provides precision control over the reduction process.
- Photochemical Reduction:
- Utilizes UV or visible light in the presence of a photocatalyst to reduce GO.
- Environmentally friendly and scalable.
- Green Reduction:
- Uses biological reducing agents like plant extracts and bacteria.
- A sustainable and eco-friendly approach.
Interesting Fact: Green reduction methods are gaining popularity due to their alignment with global sustainability goals.
Key Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
- Electrical Conductivity: Excellent, due to restored sp hybridization in the carbon lattice.
- Thermal Resistance: Retains heat resistance properties from graphene.
- Transparency: Optically transparent, making it suitable for coatings and displays.
- Water Insolubility: Non-dispersible in water due to reduced hydrophilic groups.
Pro Tip: rGO’s properties can be fine-tuned by varying the reduction method, allowing for customization in different applications.
Applications of Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
- Sensors:
- Used in biomedical, chemical, and environmental sensing to detect minute changes accurately.
- Energy Storage:
- Integral in lithium-ion batteries, supercapacitors, and photovoltaic cells due to its high conductivity and surface area.
- Electronics:
- Ideal for creating PCBs, conductive films, and coatings due to its superior electrical properties.
- Composites:
- Enhances mechanical and thermal properties when mixed with polymers, paving the way for stronger, lightweight materials.
rGO-based supercapacitors offer rapid charging capabilities and extended lifespans compared to traditional energy storage systems.
From Graphene Oxide to Reduced Graphene Oxide:
- Heating: Heat graphene oxide (GO) to high temperatures to remove oxygen and improve conductivity.
- Chemicals: Use reducing agents like hydrazine or vitamin C to convert GO to rGO in solution.
- Electricity: Apply voltage to GO, reducing it to rGO electrochemically.
- Light: Shine strong light or lasers on GO to heat and reduce it.
Bonus Insight: Each stage in this process can be optimized to influence the quality and properties of the resulting rGO.
Why Choose Adnano Technologies for rGO?
- Expertise: Skilled professionals in customization and quality control.
- Global Reach: Catering to industries worldwide with competitive pricing.
- Customer Focus: Offering research and industrial-grade rGO tailored to client needs.
Conclusion
Reduced graphene oxide continues to expand its applications in innovative technologies, including advanced energy storage, flexible electronics, and next-generation composites. As research progresses, we can expect even more groundbreaking uses for this versatile material, making it a cornerstone of material science.
To buy rGO , click here
